Knowledge Center
To hire yourself or engage Head Hunter
Whenever a vacancy arises in your organization; the question is do you source via your own recruitment department (should you have one) or do you connect with an external agency?
Obviously that decision is depending on the level and required skillset of the candidate you’re looking for.
With an economy that recovers from the various crises we have been facing over the last 8 years, companies start looking for new potential candidates to grow their business.
New external candidates can bring a lot of changes with innovative ideas and creative skills and innovative ideas to drive your business growth.
These external candidates however are not visible or available on job boards, they are happy in their current job and don’t look for a career change. Contacting these individuals requires a great sensitivity to convince them to take up new opportunities.
These hidden talents can be found only through references and a having wide network.
Ask yourself the question; is your HR department or your recruitment department well equipped to find these people and more important; do they have the time to do this in-depth search?
In some cases the best way to fill a position may be a promotion, or a lateral move from one function to another; however; still there are reasons why an organization might decide to look external to fill a critical leadership role.
Here’s some food for thought:
Create diversity in your leadership team
What I mean here is diversity in the widest sense, ethnics, race, gender etc., Make sure your employees and customers feel supported and represented within the senior ranks of the company, is some situations this is a critically strategic component to decide for external recruitment
Competition is better
It’s frustrating to find out that your competitors have some great talented people that you are weary of hearing about from your customers and prospects.
Leadership maturity gap
Even with a strong succession planning program in place, the suitable internal candidate may not be ready for a role that needs filling at a certain moment. In those situations I would highly recommend to identify and recruit an external candidate who is also able to lead with wisdom and competency. That way he/she can preparing the internal successor for a seamless future transition.
Geographical or market/technology expansion
If your organization needs expertise that it does not have internally to support or expand in a certain country/region or market/technology, it will generally recruit beneficially from the outside by hiring managers who have already established an expertise in that specific region or that specific market that aligns with your business plan.
Take the talent
In many instances where companies want to grow they consider the acquisition of a business to meet that need. However; acquisitions are costly in terms of both time and dollars, and in some instances, the employees who made that business valuable leave as soon as possible after the acquisition. There is an alternative; cheaper and faster: take their talent!
Change your company culture
Cultural alignment is the most critical component in an overall hiring strategy. Every company has a culture and that culture will be either set intentionally by the leadership team or unintentionally by the strong personalities randomly placed within the organization. Wise leadership develops a model for future cultural expectations and then intentionally works to recruit leaders who will become the champions of that model.
One remark here….too many times when a company is recruiting, the leadership team works to identify candidates who will be a strong cultural match. But what if the company has a culture that it does not want to grow? What if that culture is broken or unproductive?
Given that cultural alignment is one of the four critical components to a successful hire (along with skill set, aspirational alignment and trustworthiness), it’s important to say that alignment does not automatically mean culturally aligning with where the company is presently, but more critically, with where the company wants to go in the future...sometimes the same as the present but sometimes very different.
There is no better time than when hiring a senior executive and no better means than hiring a senior executive to begin shifting company culture.
The most important factor, of course, is selecting the best candidate for the job.
When deciding to fill in a vacant position most organizations will obviously consider both options in the selection process. The most important factor remains selecting the right fit.
Engagement Pyramid- Creating An Engaged & High Performance Culture
Culture is not only an effective enabler but a powerful driver to achieve maximal people performance and outcomes.
However, most organizations do not focus on this aspect at all and run amok around and get frantic to identify issues with processes, quality of talent and their motivation or something else. Business Leaders should design their organizations with effective Culture Heads and managers who will ensure creating an energised and motivated work place.
Introduction
The time has come to transform engagement work from surveys and business cases to concrete and specific actions to ignite and sustain engagement with results and relationships to achieve organizational and individual objectives.
The pyramid of employee engagement is an eclectic and evidence-based model outlining the tools and practices for robust employee engagement. When we are equipped with the practices and tools of the pyramid, employee engagement is never more than 10 blocks away.
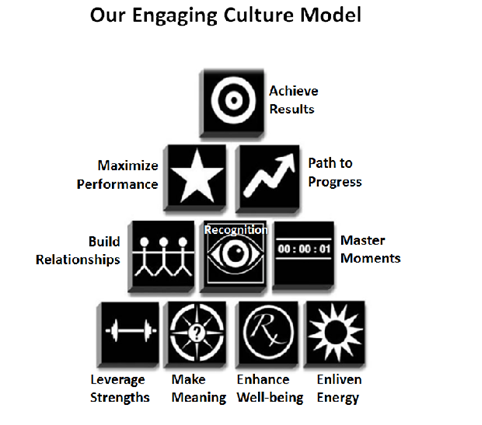
The Engagement pyramid is a bold model for employee engagement. The blocks starting at the top and going down the pyramid from left to right are: achieve results, maximize performance, path progress, build relationships, foster recognition, master moments, leverage strengths, make meaning, enhance wellbeing, and enliven energy.
The Broken Pyramid


There are at least twenty-three possible symptoms when we fail to build a pyramid of engagement within our organization.
1. There is a lack of clarity of results or even a lack of results
2. Too many results are attempted without enough capacity
3. Results are clear but lack any meaning or significance for employees
4. Performance is reduced to a management system rather than the daily lifeblood of work
5. There is a failure to hold engaging conversations when performance fails to meet expectations
6. The connections between performance and results are weak or non-existent
7. There are too many people and structural barriers to progress
8. Setbacks trump progress and managers fail to maximize the benefits of progress to engage knowledge worker
9. Collaboration tends to result in setbacks and disengaging interactions
10. Relationships are sacrificed in the name of results
11. Relationships are viewed as mushy unimportant stuff or depersonalized as human capital
12. Social media within the organization fails to align with engagement and employees’ participation in social media is an indication of disengagement
13. Individuals and organizations suffer people-myopia, barely noticing each other, and failing to voice recognition for each other
14. Moments for engagement are frittered away as small and insignificant rather than small and significant opportunities for engagement
15. Large scale programs and initiatives are launched before pilot testing and feedback from small bets or small wins
16. The ideal state of flow into work is squeezed out by anxiety and boredom
17. Eighty per cent of attention is focused on weakness, problems, gaps, failures, and inadequacies 18. Strengths are addressed as a short assessment tool that merely gives you a list of five strong personal characteristics
19. There is no compelling why to work
20. The return to individuals for work contribution is reduced to an hourly rate or salary
21. The organization and individuals fail to create and find wellbeing within work
22. Mental, emotional, and organizational energy is frittered away and work is an energy drain not an energy gain.
23. The raw material of energy for engagement is under utilized
The benefits of the pyramid
There are a number of benefits in applying this unique model of employee engagement.
The model is simple. The model can be grasped within seconds and with 10 blocks and bold images it is quickly understood by many managers and other employees. The images and the pyramidal structure make it easy to visualize and easy to recall. Yet, embedded within this simplicity are 10 powerful keys to create, sustain, and enhance employee engagement.
The model is unique. Each element of the model has a bold image to represent the foundation of that block. There is a target for results, an arrow for progress, a compass for meaning, and a clock for moments. The 10 icons add a strong visual dimension to the model.
The structure is inspirational. The model was inspired by the work of the Egyptian pyramids and former U.C.L.A. winning basketball coach John Wooden’s pyramid of success. The pyramids in Egypt demonstrate that the structure will stand the test of time and remain for years. We all know the pyramids were not built in one day.
John Wooden’s pyramid outlined 15 building blocks for success and was the structure behind Wooden’s phenomenal coaching success with U.C.L.A.’s basketball program and the legacy of his work with players. The Wooden pyramid is still inspiring many players and coaches.
The pyramid of engagement model is flexible. The pyramid is open to individuals or organizations shifting the blocks around. For example someone may want to put relationships as the top of the pyramid and results at the heart of the pyramid. Someone else may have their own block they would like to switch with one of the blocks in the original pyramid. Although the model is solid, it is not static.
The pyramid offers the big picture of what can be done for engagement while offering the ability and structure to tackle one block at a time. Many people are overwhelmed by work and perceive engagement as yet another task. With this model you can focus on just one block at a time for a day, a week, a month, or even a year.
The model can be used by leaders, managers, and supervisors to foster engagement or heighten their own engagement. The pyramid was originally designed for managers to use as a tool to increase engagement with employees who report to them. It quickly became apparent that the model can be used by managers to enhance their own engagement or be offered to employees as a tool to take charge of their engagement. We can only engage others when we are engaged.
Many organizations are organized around a pyramid. The CEO or President is at the top and people are on levels below the CEO. We should stop putting people into pyramids (remember what they were used for in Egypt) rather this pyramid is based on elements and everyone can work towards results, performance, relationships, etc. We build the blocks of engagement together, not alone, and the apex of the pyramid is a place for all of us.
We can build a mini pyramid of 3 blocks for focused effort. It is easy to make mini pyramids out of the 10 blocks. I believe when we try to focus on more than 3 items at a time we end up getting confused and diffusing our efforts. For example, you could take the top 3 blocks and focus on results, performance, and progress. You can do an assessment of your strengths and weaknesses and build a mini pyramid to overcome weaknesses or build a mini pyramid to get the absolute most from your engagement strengths. Often as you work with one block you are having an impact on many other blocks of the model.
The blocks are based on research and evidence based practice. Just three examples are the research by Teresa Amabile on progress, setbacks and meaning; research by Jane Dutton on organizational energy; and research by Gallup on strength based approaches to work and wellbeing.
GROWTHMODE can help organizations develop a high performance and engaged culture by implementing this pyramid engagement model.
Maximize Your People Process Effectiveness
At GrowthMode, we help organizations enhance the effectiveness of their people processes by implementing the highly effective PCMM framework. This model though initially embraced by the IT / ITES industries later on is a most sought after framework to achieve HR Process Excellence.
The People Capability Maturity Model (short names:People CMM, PCMM,P-CMM) is a maturity framework that focuses on continuously improving the management and development of the human assets of an organization. It describes an evolutionary improvement path from ad hoc, inconsistently performed practices, to a mature, disciplined, and continuously improving development of the knowledge, skills, and motivation of the workforce that enhances strategic business performance. The People Capability Maturity Model (People CMMI) is a framework that helps organizations successfully address their critical people issues. Based on the best current practices in fields such as human resources, knowledge management, and organizational development, the People CMM guides organizations in improving their processes for managing and developing their workforces. The People CMM helps organizations characterize the maturity of their workforce practices, establish a program of continuous workforce development, set priorities for improvement actions, integrate workforce development with process improvement, and establish a culture of excellence. Since its release in 1995, thousands of copies of the People CMM have been distributed, and it is used worldwide by organizations, small and large. First published in book form in 2001, it is in print in several editions worldwide, and a second edition was published in July 2009.
Characterize the maturity of their workforce practices
Set priorities for immediate action
Integrate workforce development with process improvement
Become an employer of choice
The term ‘Staffing’ relates to the recruitment, selection, development, training and compensation of the managerial personnel. Staffing, like all other managerial functions, is the duty which the apex management performs at all times. In a newly created enterprise, the staffing would come as a. third step—next to planning and organizing—but in a going enterprise the staffing process is continuous.
In order to define and clarify the group of employees included in the staffing concept, it must be stated that the staffing function is concerned with the placement, growth and development of all of those members of the organization whose function it is to get things done through one effort of other individuals.
This definition includes all levels of management because those who will occupy positions in the top two or three levels of management fifteen or twenty years from now are likely to be found in the lower levels today.
“The managerial function of staffing involves manning the organisational structure through effective and proper selection, appraisal, and development of personnel to fill the roles designed into the structure.” — Koontz and O’Donnell
Nature of Staffing:
Staffing is an integral part of human resource management. It facilitates procurement and placement of right people on the right jobs.
The nature of staffing function is discussed below:
1. People Centred:
Staffing is people centred and is relevant in all types of organisations. It is concerned with all categories of personnel from top to bottom of the organisation.
The broad classification of personnel may be as follows:
(i) Blue collar workers (i.e., those working on the machines and engaged in loading, unloading etc.) and white collar workers (i.e., clerical employees).
(ii) Managerial and non-managerial personnel.
(iii) Professionals (such as Chartered Accountant, Company Secretary, Lawyer, etc.).
2. Responsibility of Every Manager:
Staffing is a basic function of management. Every manager is continuously engaged in performing the staffing function. He is actively associated with recruitment, selection, training and appraisal of his subordinates. These activities are performed by the chief executive, departmental managers and foremen in relation to their subordinates. Thus, staffing is a pervasive function of management and is performed by the managers at all levels.
It is the duty of every manager to perform the staffing activities such as selection, training, performance appraisal and counseling of employees. In many enterprises. Personnel Department is created to perform these activities.
But it does not mean that the managers at different levels are relieved of the responsibility concerned with staffing. The Personnel Department is established to provide assistance to the managers in performing their staffing function. Thus, every manager has to share the responsibility of staffing.
3. Human Skills:
Staffing function is concerned with training and development of human resources. Every manager should use human relations skill in providing guidance and training to the subordinates. Human relations skills are also required in performance appraisal, transfer and promotion of subordinates. If the staffing function is performed properly, the human relations in the organisation will be cordial.
4. Continuous Function:
Staffing function is to be performed continuously. It is equally important in the established organisations and the new organisations. In a new organisation, there has to be recruitment, selection and training of personnel. In a running organisation, every manager is engaged in various staffing activities. He is to guide and train the workers and also evaluate their performance on a continuous basis.
Importance of Staffing:
It is of utmost importance for the organisation that right kinds of people are employed. They should be given adequate training so that wastage is minimum. They must also be induced to show higher productivity and quality by offering them incentives.
In fact, effective performance of the staff function is necessary to realize the following benefits:
1. Efficient Performance of Other Functions:
Staffing is the key to the efficient performance of other functions of management. If an organisation does not have competent personnel, it can’t perform planning, organisation and control functions properly.
2. Effective Use of Technology and Other Resources:
It is the human factor that is instrumental in the effective utilisation of latest technology, capital, material, etc. the management can ensure right kinds of personnel by performing the staffing function.
3. Optimum Utilisation of Human Resources:
The wage bill of big concerns is quite high. They also spend money on recruitment, selection, training and development of employees. In order to get the optimum output from the personnel, the staffing function should be performed in an efficient manner.
4. Development of Human Capital:
The management is required to determine the manpower requirements well in advance. It has also to train and develop the existing personnel for career advancement. This will meet the requirements of the company in future.
5. Motivation of Human Resources:
The behaviour of individuals is shaped by many factors such as education level, needs, socio-cultural factors, etc. that is why, the human aspect of organisation has become very important. The workers can be motivated through financial and non-financial incentives.
6. Building Higher Morale:
Right type of climate should be created for the workers to contribute to the achievement of the organisational objectives. By performing the staffing function effectively, management can show the significance it attaches to the personnel working in the enterprise. This will increase the morale of the employees.
